INTRODUCTION
Mortality is the most important entity that mankind has not been able to conquer, now that I think about it, mankind has not been able to achieve time travel despite how much resource and money that has been put into it, there are few stuffs that man has not been able to achieve but I think to be able to conquer Death has to be the most important.
Everyone especially powerful people (including me) wants to live forever, despite the fact that we all want to go to heaven, nobody wants to die and this has proven to be impossible by nature time and again. Despite this, Rich and influential people has spent Trillions of Dollars to funds research that are pro immortal and these research always end up with the same results IMMORTALITY CANNOT BE ACHIEVED.
Recently, Jeff Bezos: The origin founder of Amazon was reported to be funding an anti aging research startup Altos Labs located in Silicon Valley, they are looking into ways to reverse aging in human cells and it was reported that even though the research is still in early stage, it has shown some promises. This has generated a lot of reactions from people including Elon Musk who put out a message on a popular platform called twitter that if the research doesn't work, then Jeff Bezos will have to sue death (hilarious right)
PROJECT PROBLEM
Looking at the insanely amount of money, energy, resource and research that mankind has spent in defeating mortality and it has not been achieved, one couldn't help but wonder if the resource and money spent is at least yielding results by decreasing mortality rate in mankind, as Healthcare technology improve and man evolve, is mortality rate in the year 2000 the same with mortality rate in the year 2020? Studying the data trend, can immortality still be achieved in the future of mankind? What factors are peculiar to countries with low mortality rate and countries with high mortality rate? What can be done to decrease mortality rate because as mortality rate decreases, the more chances man have to defeat it.
DATA
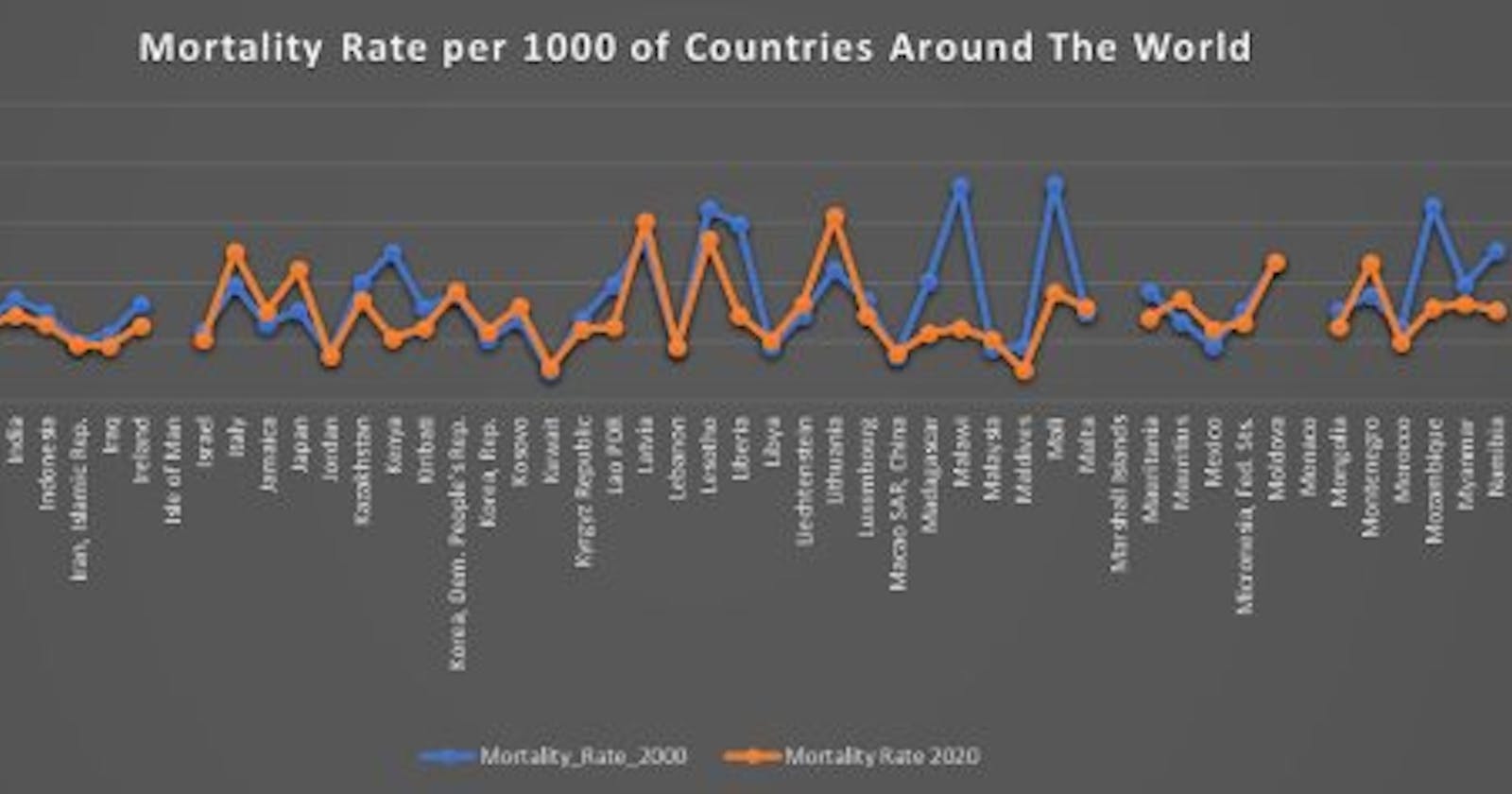
For this, the data used was gotten from World Bank Data includes Mortality Rate gotten from Over 250 countries over the span of over 50years, but data of recent years between 2000-2020 was analyzed using Microsoft Excel to get insights. The data metric was Mortality Rate per 1000 People.
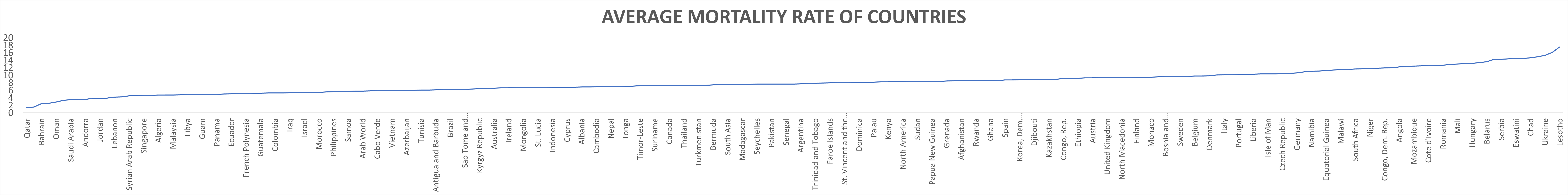
The average mortality rate of each countries was analyzed and sorted and then visualized.
It was discovered that the top ten countries with the lowest mortality rate includes;
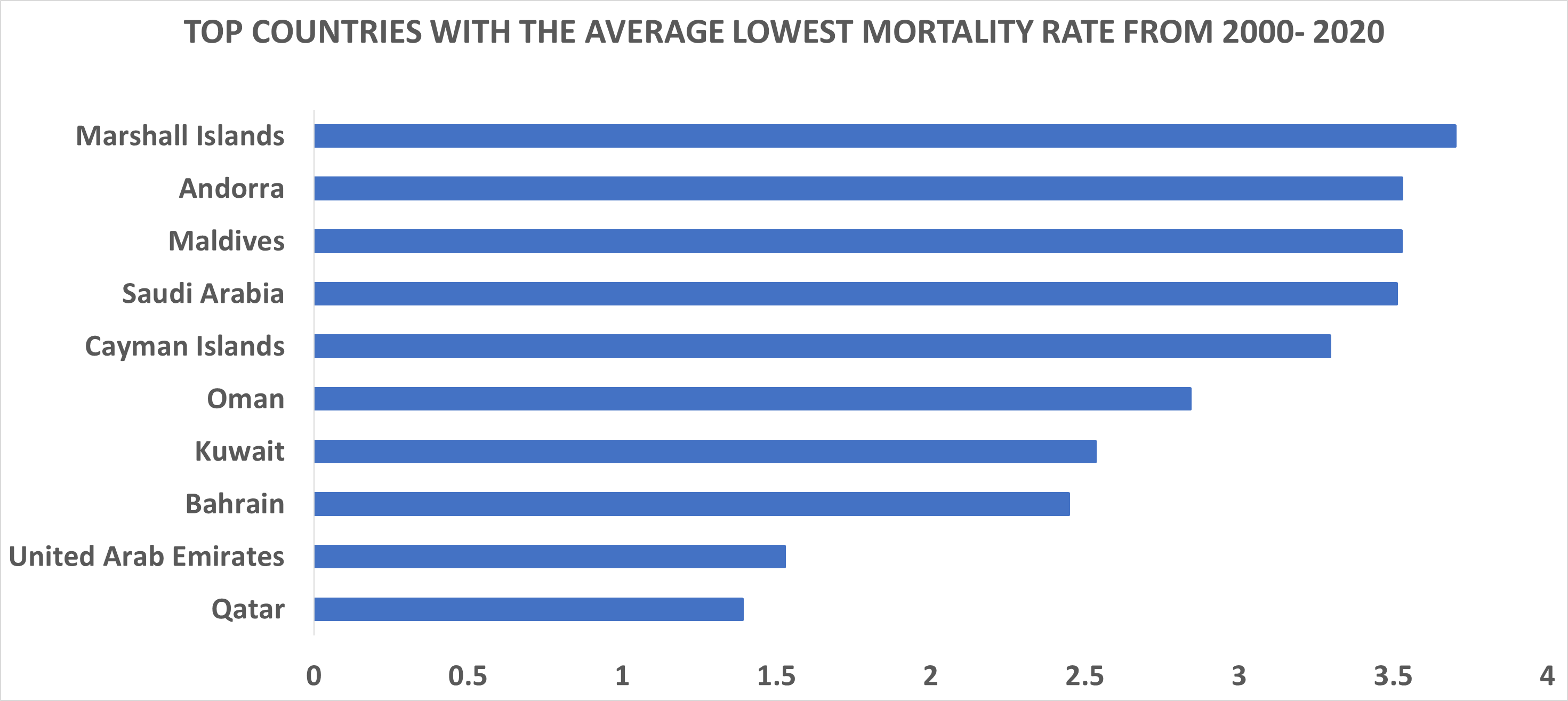
1). Qatar: Qatar is located in the Middle East, it is ranked fourth wealthiest country in the year 2022. Qatar citizens also known as Qatari have average life expectancy of 77 years for Males and 81 years for females. Qatar government invest heavily in Healthcare as they have great healthcare facility as have been quoted to have the best health system during Covid19 by Abdinasir Abubakar from World Health Organization regional office for Eastern Mediterranean.
Healthcare standards in Qatar are generally high. Qataris are covered by a national health insurance scheme, while expatriates must either receive health insurance from their employers, or in the case of the self-employed, purchase insurance. Qatar's healthcare spending is among the highest in the Middle East, with $4.7 billion being invested in healthcare in 2014. This has made Healthcare cheap and easily accessible to all citizen and non citizens regardless of their socio economic background and Health conditions
2). United Arab Emirates: Also located in the middle east, UAE is Ranked 7th most richest country in the world in the year in 2022. It shares border with Oman and Saudi Arabia. The UAE has a comprehensive, government-funded health service and a rapidly developing private health sector that delivers a high standard of health care to the population.
Most infectious diseases like malaria, measles and poliomyelitis that were once prevalent in the UAE have long been eradicated. Life expectancy in the UAE is 77.8 years, achieving levels similar to Europe and North America. The United Arab Emirates has universal healthcare, with healthcare provided for all nationals and mandatory health insurance for citizens of other countries. Employers are required to provide health insurance for expatriate workers. In the UAE employers must also provide health insurance for up to one spouse and three dependents, while in Dubai expats are required to provide insurance for their dependents. Additionally, a charitable fund helps underinsured expatriates finance more serious medical conditions such as cancer, dialysis, polytrauma and disability. All these are responsible for the low death rate of both citizens and non citizens of UAE. The World bank ranked Dubai and Abu Dhabi as being the 2nd and 3rd, respectively, most popular medical tourism destinations in the region as they have taken steps in recent years to ensure world-class healthcare is accessible for all and encourage innovation in medical field.
3). Bahrain: this country is located between Saudi Arabia and Qatar. They are also one of the richest country in the world. They invest heavily in public welfare, infrastructure, public sector ,public and private Healthcare. This led to a steady increase in life expectancy. Bahrainis women life expectancy is 81.8 years and their male counterpart life expectancy is 77.1 years. It is interesting to note that their life expectancy increased significantly in 1960s after they discovered oil in 1931 this boosted their economic growth and after which they invested in public health care which boosted their life expectancy. Healthcare is free of charge for Bahrainis at government hospitals and health centers across all governorates, and available for a nominal fee for non-Bahrainis. Under the National Social Health Insurance Program (Sehati), Bahrainis and domestic workers receive free health coverage from the government, while other expatriate employees are covered by their employers.
- Now i am beginning to think countries located in the Middle east had a deal with God that the rest of us do not know about
4). Kuwait: It is officially known as the State of Kuwait, is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Arabian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the north and Saudi Arabia to the south. It is in 31st position of world richest country, Kuwait has a state-funded healthcare system, which provides treatment without charge to holders of a Kuwaiti passport. A public insurance scheme exists to provide reduced cost healthcare to non-citizens. Private healthcare providers also run medical facilities in the country, available to members of their insurance schemes.
5). Oman: officially known as the Sultanate of Oman, Oman is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. Ranking 56th position of the richest countries in the world, the Omanis have a high life expectancy of 73.8 years. Omani nationals have free access to the country's public health care, though expatriates typically seek medical care in private sector clinics and hospitals. Generally, the standard of care in the public sector is high for a middle-income country.
6). Cayman Island: The Cayman Islands is a British Overseas Territory which encompasses three islands in the western Caribbean Sea. It is a tourist country with few thousands people population. In 2003, the Cayman Islands became the first country in the world to mandate health insurance for all residents. This has made Health care accessible for all citizen, non citizens have to acquire health insurance or use private healthcare in order to have access to healthcare.
7). Saudi Arabia: this country located in Middle East and it is ranked 27th most richest country in the world. They invested heavily in health both private and public sector and their government provide free universal health care for their citizens.
8). Maldives: officially known as the Republic of Maldives, it is an archipelagic state located in Southern Asia, situated in the Indian Ocean. It is ranked the 62th wealthiest country in the world, The Maldives has universal health insurance that covers a plethora of primary care services and it receives funding from the Maldives’ government. Notably, they pays for citizens to go abroad for certain medical treatments if the treatments are not available in the Maldives. According to a 2018 report from the World Health Organization (WHO), 9% of the Maldives’ GDP goes toward healthcare. The country spends a higher percentage of its GDP on healthcare than any country in Southeast Asia, where the average expenditure , for the region is 3.46%.The Maldives has an above-average life expectancy. The life expectancy in the Maldives was 78.6 years in 2019, while the world average the same year was 72.6. Healthcare in the Maldives is rapidly improving, with the country having an above-average life expectancy and basic health services on all inhabited islands. However, some areas of the nation struggle to receive essential medical supplies and medicine can be expensive
9). Andorra: Andorra is an European country located between France and Spain in the Pyrenees mountains. The economy of Andorra is a developed and free market economy driven by finance, retail, and tourism. Healthcare in Andorra is provided to all employed persons and their families by the government-run social security system, Caixa Andorrana de Seguretat Social, which is funded by employer and employee contributions in respect of salaries. The cost of healthcare is covered at rates of 75% for outpatient expenses such as medicines and hospital visits, 90% for hospitalization, and 100% for work-related accidents. The remainder of the costs may be covered by private health insurance. Other residents and tourists require full private health insurance.
10). Brunei Darussalam: Brunei , formally Brunei Darussalam, is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It is in the top 10 wealthiest countries in the world in 2022. Brunei's healthcare system is managed by the Brunei Ministry of Health and funded by the General Treasury. Healthcare in Brunei is charged at B$1 per consultation for citizens and is free for anyone under 12 years old. The government covers the cost of sending citizens overseas to access treatments and facilities not available in the country. In 2011–2012, 327 patients were treated this way in Malaysia and Singapore at a cost of $12 million.
TOP TEN COUNTRIES WITH HIGHEST MORTALITY RATE
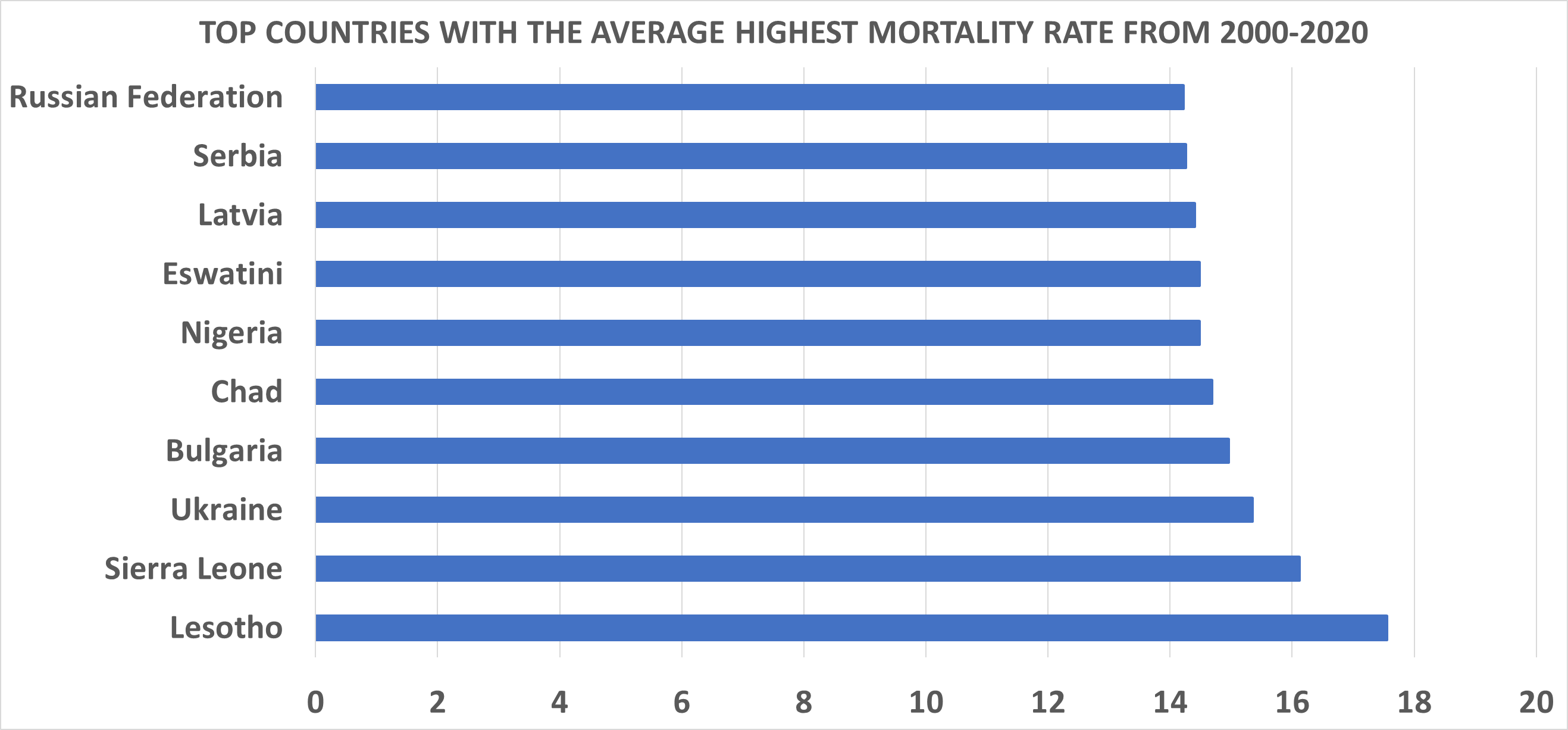
1). Lesotho: Lesotho, a high-altitude, landlocked kingdom encircled by South Africa. The World Bank classifies Lesotho as a lower-middle-income country. Health care services in Lesotho are delivered primarily by the government and the Christian Health Association of Lesotho. Access to health services is difficult for many people, especially in rural areas. The country’s health system is challenged by the relentless increase of the burden of disease brought about by AIDS, and a lack of expertise and human resources. Serious emergencies are often referred to neighboring South Africa. The largest contribution to mortality in Lesotho are communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions.
2). Sierria Leone: Sierra Leone is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean. Sierra Leone is among the poorest countries in the world today with about 72.5 percent of its total population living in poverty. Healthcare in Sierra Leone is generally charged for and is provided by a mixture of government, private and non-governmental organizations. Sierra Leone has long struggled with some of the world’s worst health outcomes—including a maternal mortality epidemic in which a woman’s lifetime risk of dying in pregnancy or childbirth is 1 in 20. Extreme poverty prevents most families from accessing health care. And often the care they need isn’t available, given the country’s severe shortage of trained clinicians, health infrastructure, and medical supplies
3). Ukraine: Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine’s economic freedom score is 54.1, making its economy the 130th freest in the 2022 Index. the country's persistently high mortality rate is due to low-quality health care, an increase in the number of epidemic diseases, and the widespread abuse of alcohol and drugs. In theory, the constitution of Ukraine guarantees free healthcare to all citizens and registered residents. However, at present, the limited public funding for healthcare means patients can obtain only basic medical services for free. They will have to pay from their pocket for medical expenses and a majority of healthcare services. To improve the funding process, various measures have been introduced in recent years. However, the desired changes in infrastructure are yet to be seen. Public healthcare facilities are available in Ukraine but their standards are not very high. Private healthcare, on the other hand, is very expensive and medical care are mostly not available in rural area.
4). Bulgaria: Bulgaria is a Balkan nation with diverse terrain encompassing Black Sea coastline, a mountainous interior and rivers, including the Danube. Bulgaria's economic freedom score is 71.0, making its economy the 29th freest in the 2022 Index. Bulgaria has a mixed public–private healthcare financing system. Healthcare is financed from compulsory health insurance contributions, taxes, out-of pocket (OOP) payments, voluntary health insurance premiums, corporate payments, donations, and external funding. The high mortality rate in Bulgaria is due to diseases of the cardiovascular system, non-infectious and cancer diseases. Lack of access for people who cannot afford to pay for the compulsory health insurance program remains persistent. This makes healthcare out of reach for poor, unemployed, rural citizens.
5) Chad: officially known as the Republic of Chad, Chad is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. Chad is one of the poorest countries in the world. Health in Chad is suffering due to the country’s weak healthcare system. Access to medical services is very limited and the health system struggles with shortage of medical staff, medicines and equipment. The life expectancy at birth for people born in Chad, is 53 years for men and 55 years for women (2016). In 2019 Chad ranked as 187 out of 189 countries on the human development index, which places the country as a low human development country.
6). Nigeria: Nigeria, an African country on the Gulf of Guinea, also known as the giant of Africa. Nigeria is Ranked 144th richest out if 192 countries. Nigeria has public, private and traditional healthcare facility. Healthcare delivery in Nigeria has experienced progressive deterioration as a result of weakened political will on the part of successive governments to effectively solve a number of problems that have long existed in the sector over many years. As of February 2018, the country was ranked 187 out of 191 countries in the world in assessing the level of compliance with the Universal Health Coverage (UHC), as very little of the populace are health insured, whereas even government provision for health is insignificant. The main causes of death in Nigeria in 2019 were neonatal disorders. More specifically, 12.25 percent of all deaths were caused by neonatal disorders. Other common causes included malaria, diarrheal diseases, and lower respiratory infections.
7). Eswatini: Eswatini, officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The Health in Eswatini is poor and four years into the United Nations sustainable development goals, Eswatini seems unlikely to achieve goal on health. As a result of 63% poverty prevalence, 27% HIV prevalence, and poor health systems, high rate of maternal and under 5 mortality resulting in a life expectancy that remains amongst the lowest in the world. Despite significant international aid, the government fails to adequately fund the health sector. Nurses are now and again engaged in demonstrations over poor working conditions, drug stock outs, all of which impairs quality health delivery. Despite tuberculosis and AIDS being major causes of death, diabetes and other non-communicable diseases are on the rise. Primary health care is relatively free in Eswatini save for its poor quality to meet the needs of the people. Road traffic accidents have also increased over the years.
8). Latvia: Latvia is a country on the Baltic Sea between Lithuania and Estonia. 2015, the country spent only 5.8% of its GDP, equal to €1,071 per capita on Healthcare. This falls considerably below the EU average of 9.9%. These statistics showcase the lingering challenges of the country’s underfunded healthcare system. Latvia needs critical adjustments in order to improve the country’s health profile. Not only is Latvia’s spending on this sector very low compared to other EU nations, but problems like obesity, smoking and alcohol consumption signal an urgent need for improvement. Ensuring equal access is also an important goal for the country to strive toward.
9). Serbia: Serbia, officially the Republic of Serbia, is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, Serbia has a comprehensive universal health system with free access to health care services at the primary level. However, some vulnerable groups face financial barriers for medical care and the current system of financing encourages inefficiency in the use of resources. Despite progress in the last decade, reforms to improve the performance and transparency of the health system are still pending.
NOTE
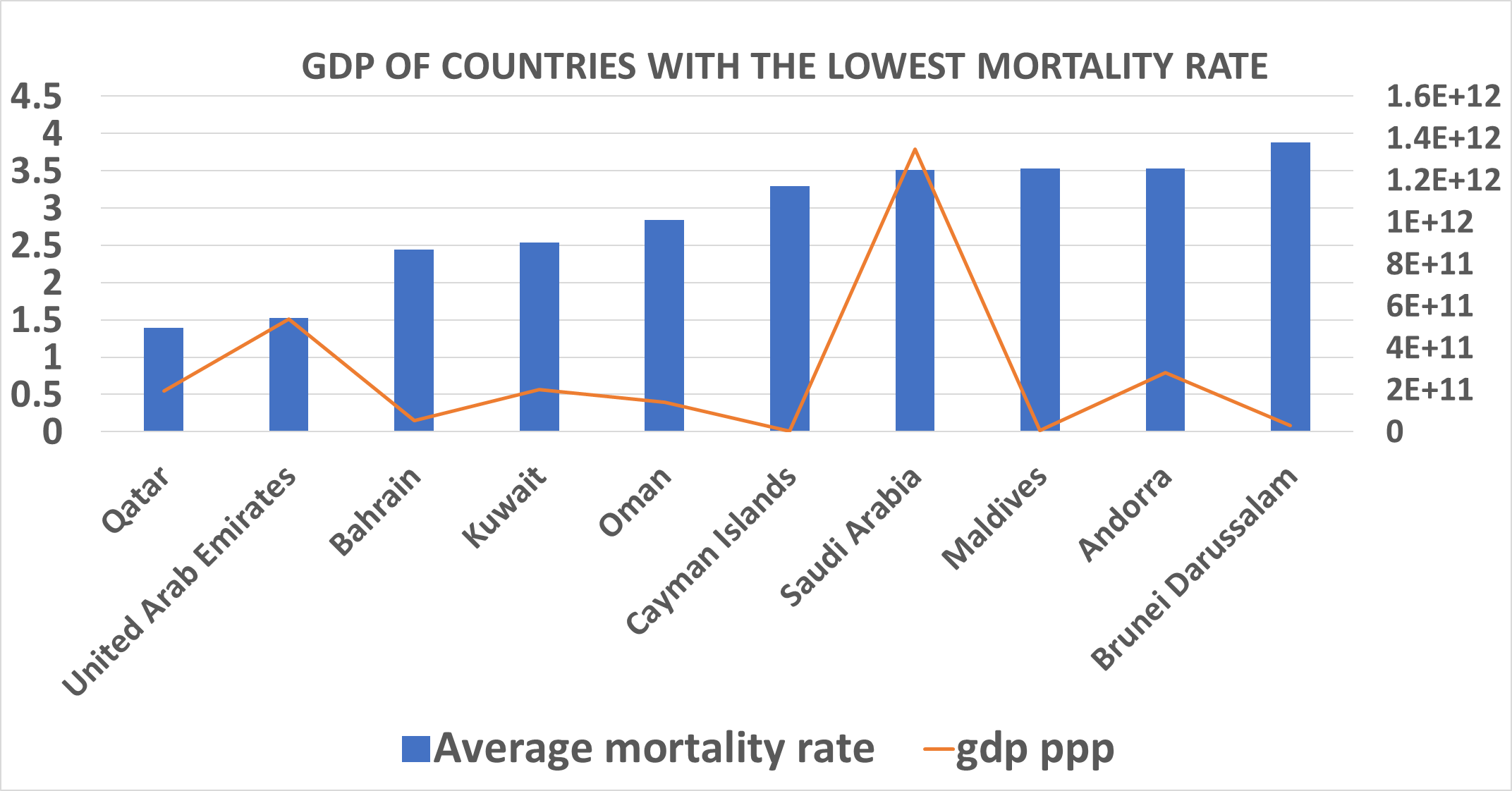
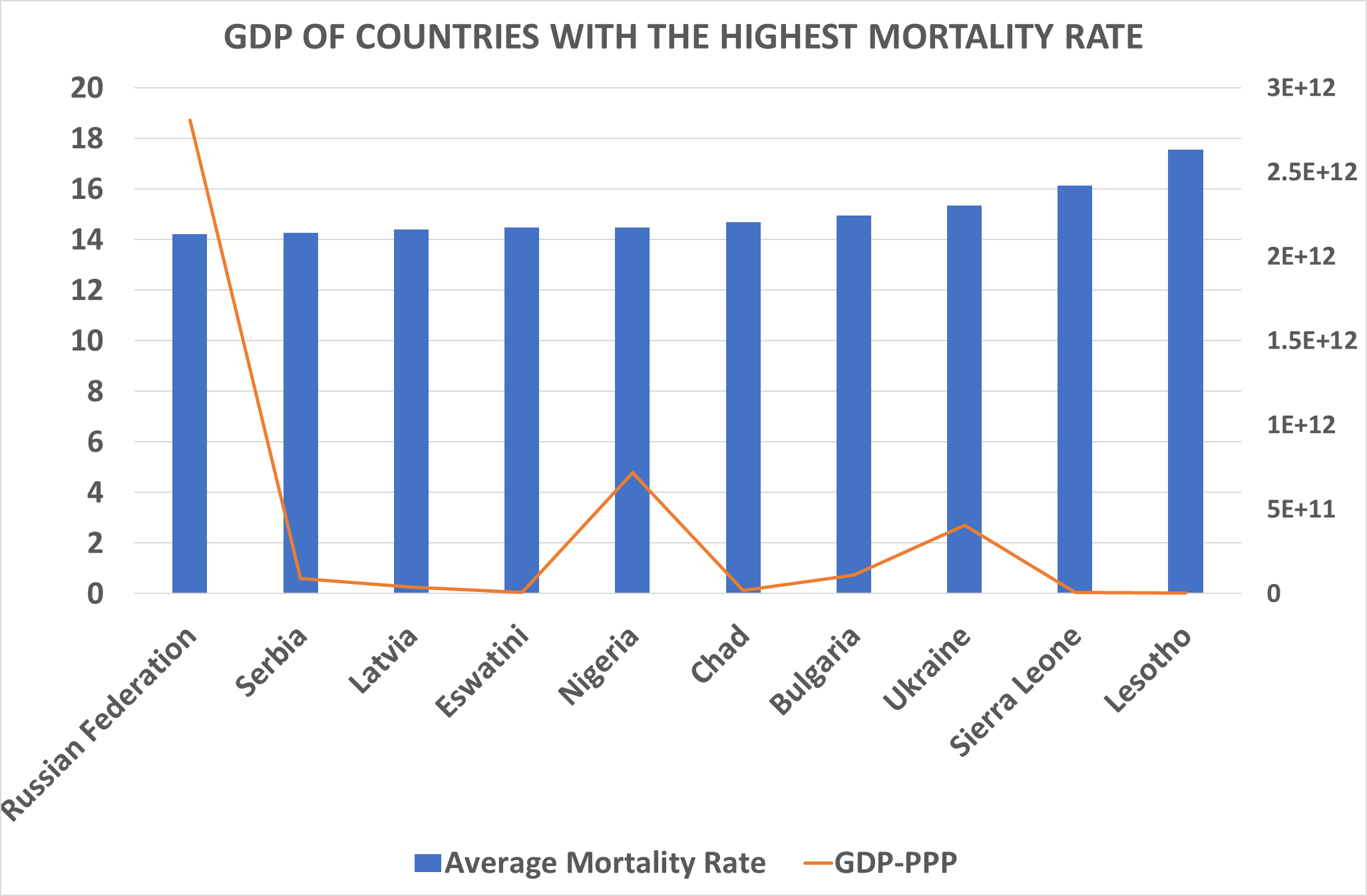
Most countries with very low mortality rate have something in common: they are all doing very well economically, in fact over 50% of the top ten countries with low mortality rates are in the top richest country in the world, this might not be the case because some countries with very high mortality rate are also doing very well economically. Going by the first assumption that economy might have an impact in mortality rate, that is, the higher the economy the lower the mortality rate has been proven to not be completely true. The fact that all the governments of countries with low mortality rate all made great efforts to invest in healthcare and make basic healthcare accessible to all and sundry in their country regardless of their socio economic background. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Bahrain et. cetera even went extra miles to make healthcare free for all citizens, all these amenities will enable low mortality in the country
On the other hand, The high mortality is due to several factors: infectious diseases, insufficient healthcare, malnutrition, cardiovascular diseases, violence, cancer diseases and accidents. The countries with high mortality and low birth rates are facing a demographic collapse. Bulgaria, together with Ukraine, Serbia, and Russia is part of this negative ranking. The government are also not helping, Country like Latvia are investing lowly into healthcare, Bulgarian government are focusing only on people who can afford healthcare and no provisions has been made for the less privileged. Nigerian Government are no longer investing as much as they used to into healthcare. Eswatini Government are embezzling financial aids. All these has shown that the government are also responsible for high mortality rate in these countries.
WORLD MORTALITY RATE OVER THE YEARS
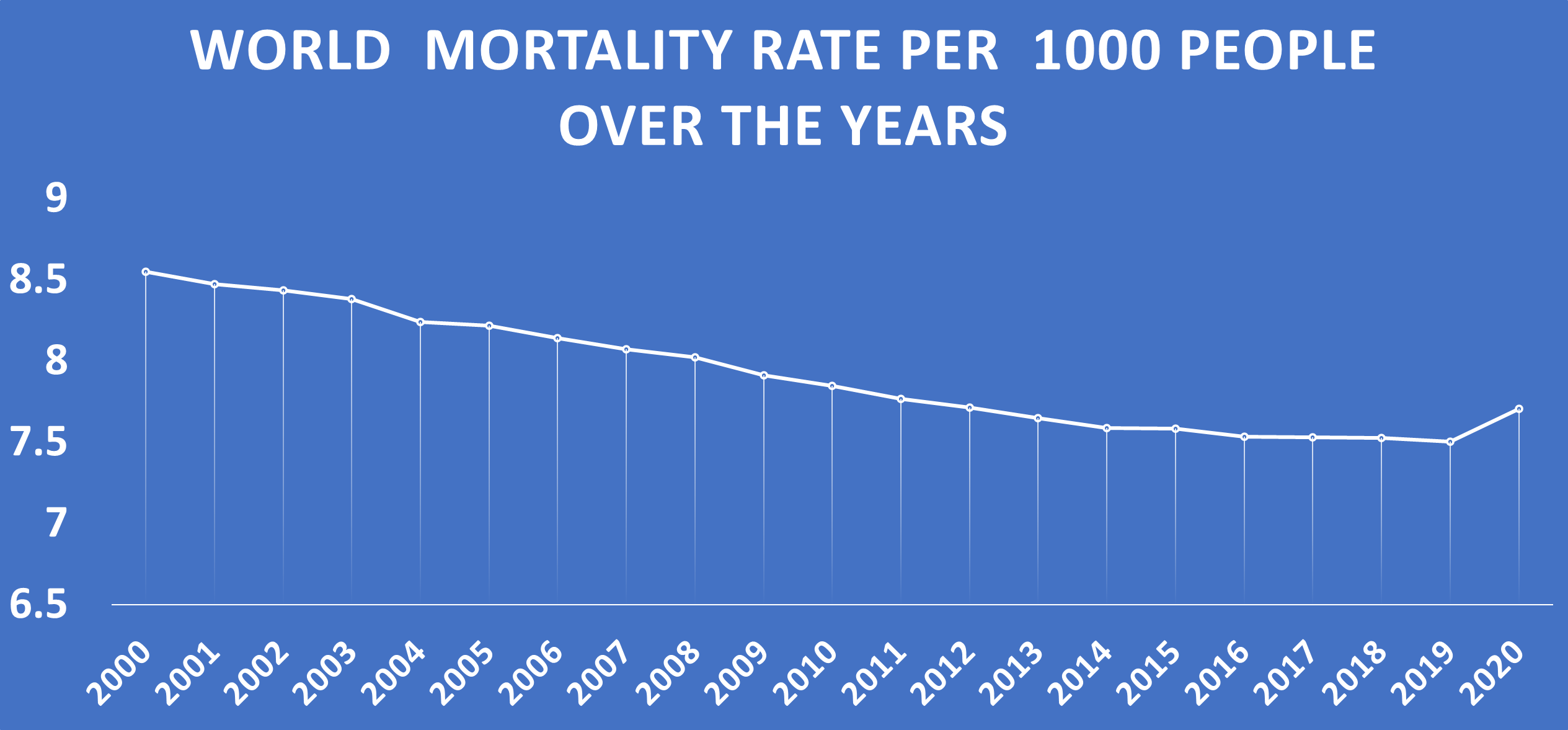
World mortality has been decreasing steadily from 2000 - 2019, and if it continues like that, there is a probability that one day humanity will defeat mortality but 2020 witnessed a spike of over 2.7% increase in mortality, this is as a result of the corona virus pandemic that occurred in 2020. This further confirms despite all the technology put in place, nature will always find a way to prove that man can never be immortal. For now, there is no technology that can make mankind defeat mortality but the good news is that mortality has greatly decreased over the years in the absence of catastrophe.
CONCLUSION
Despite the fact that mortality cannot be defeated, it can be reduced and we all have a role to play for this to be achieved, Government should provide quality healthcare for all their citizens regardless of their social status, Healthcare should be accessible to people especially in people living rural area. Government should also invest in public welfare for citizens as this would decrease the rate of poverty and thereby improving quality of life People should try as much as possible to eat healthy as this would decrease the rate of cancer disease, kidney disease and infection and others. People should decrease the intake of alcohol and drugs as this will decrease cardiovascular diseases, violence. Man should embrace peace always and avoid war. All these when put in place and followed religiously will help in the continual decrease in mortality rate of mankind
I HOPE YOU ENJOY READING THIS AS MUCH AS I ENJOYED WRITING IT
P.S: I still believe that one day, humanity will conquer death ( because some of us deserve to live forever)